Request Demo
Last update 29 Jan 2026

Hebei Medical University
Last update 29 Jan 2026
Overview
Basic Info
Introduction Hebei Medical University is a prestigious institution located in Shijiazhuang, Hebei province. Founded in 1894, it is one of the oldest medical schools in China and has been awarded an AAA grade. |
Tags
Other Diseases
Nervous System Diseases
Neoplasms
Small molecule drug
Radiopharmaceuticals and diagnostic agent
Chemical drugs
Disease domain score
A glimpse into the focused therapeutic areas
No Data
Technology Platform
Most used technologies in drug development
No Data
Targets
Most frequently developed targets
No Data
| Top 5 Drug Type | Count |
|---|---|
| Small molecule drug | 17 |
| Radiopharmaceuticals and diagnostic agent | 2 |
| circular RNA | 1 |
| Chemical drugs | 1 |
| Non-degrading molecular glue | 1 |
| Top 5 Target | Count |
|---|---|
| HDAC6(Histone deacetylase 6) | 3 |
| HBsAg | 1 |
| MUT x mTOR | 1 |
| HDAC8(Histone deacetylase 8) | 1 |
| Kv7.2 x Kv7.3 | 1 |
Related
25
Drugs associated with Hebei Medical UniversityTarget |
Mechanism β-lactamase inhibitors |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication- |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date- |
Mechanism 5-HT receptor modulators [+3] |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication |
Drug Highest PhasePhase 1/2 |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date- |
Target- |
Mechanism Stem cell replacements |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication- |
Drug Highest PhasePhase 1/2 |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date- |
443
Clinical Trials associated with Hebei Medical UniversityNCT07370116
Safety and Feasibility of Omitting Nasogastric Decompression in Minimally Invasive Pancreaticoduodenectomy: a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
This study will evaluate two perioperative nasogastric tube strategies in patients undergoing laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy. The goal is to determine whether routine omission of a nasogastric tube is not worse than routine nasogastric tube placement in terms of overall complications and postoperative recovery.
Participants will be randomly assigned to one of two groups. Each group will receive the assigned nasogastric tube strategy during and after surgery, and will be followed during the hospital stay and after discharge for up to postoperative 90 days. Information will be collected from routine clinical care, including discomfort score, symptoms, imaging or laboratory tests when clinically indicated, and postoperative outcomes.
The main outcome of this study is the overall burden of postoperative complications within 30 days after surgery, measured using the Comprehensive Complication Index, which summarizes all complications into a single score. Secondary outcomes include rates of pancreas surgery-specific complications (such as delayed gastric emptying, pancreatic fistula, bile leak, bleeding, and chyle leak), other abdominal and pulmonary complications, and organ dysfunction (including kidney injury, sepsis, and new cardiac dysfunction). The study will also evaluate patient discomfort related to the nasogastric tube (pain/discomfort scores), the need for nasogastric tube reinsertion, postoperative recovery milestones (ability to resume oral intake and length of hospital stay), healthcare costs, and all-cause mortality at 30 and 90 days after surgery.
Participants will be randomly assigned to one of two groups. Each group will receive the assigned nasogastric tube strategy during and after surgery, and will be followed during the hospital stay and after discharge for up to postoperative 90 days. Information will be collected from routine clinical care, including discomfort score, symptoms, imaging or laboratory tests when clinically indicated, and postoperative outcomes.
The main outcome of this study is the overall burden of postoperative complications within 30 days after surgery, measured using the Comprehensive Complication Index, which summarizes all complications into a single score. Secondary outcomes include rates of pancreas surgery-specific complications (such as delayed gastric emptying, pancreatic fistula, bile leak, bleeding, and chyle leak), other abdominal and pulmonary complications, and organ dysfunction (including kidney injury, sepsis, and new cardiac dysfunction). The study will also evaluate patient discomfort related to the nasogastric tube (pain/discomfort scores), the need for nasogastric tube reinsertion, postoperative recovery milestones (ability to resume oral intake and length of hospital stay), healthcare costs, and all-cause mortality at 30 and 90 days after surgery.
Start Date01 Mar 2026 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
NCT07337551
Gossypol Acetate Combined With Bevacizumab and FOLFIRI as Second-Line Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer With TP53 Mutation and LRPPRC Positivity: A Single-Center, Single-Arm Clinical Study
This study is a single-center, single-arm clinical trial involving patients with TP53-mutated and LRPPRC-positive metastatic colorectal cancer. It aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gossypol acetate tablets combined with bevacizumab and the FOLFIRI regimen as a second-line treatment. The study is based on a key scientific finding: LRPPRC is a critical protein mediating chemotherapy resistance induced by TP53 mutation, and gossypol acetate-an existing drug-can specifically degrade LRPPRC. Preclinical studies have demonstrated its potential to effectively reverse drug resistance.
Patients who have experienced failure of first-line oxaliplatin-based therapy are planned to be enrolled. All eligible subjects will receive the same combined treatment regimen until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. The primary endpoint is objective response rate (ORR), and secondary endpoints include progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. Throughout the treatment period, patients will undergo regular tumor imaging evaluations and safety monitoring. Statistical analyses will be performed using both the full analysis set and the per-protocol set.
This study strictly adheres to ethical standards and aims to explore a new potential treatment strategy for this specific refractory patient population.
Patients who have experienced failure of first-line oxaliplatin-based therapy are planned to be enrolled. All eligible subjects will receive the same combined treatment regimen until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. The primary endpoint is objective response rate (ORR), and secondary endpoints include progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. Throughout the treatment period, patients will undergo regular tumor imaging evaluations and safety monitoring. Statistical analyses will be performed using both the full analysis set and the per-protocol set.
This study strictly adheres to ethical standards and aims to explore a new potential treatment strategy for this specific refractory patient population.
Start Date01 Feb 2026 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
ChiCTR2500113612
Individualized Blood Pressure Management Based on Multimodal Brain Function Monitoring:The Impact of Willis Circle Compensation Capacity on Postoperative Delirium and Stroke in CEA Patients
Start Date01 Jan 2026 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
100 Clinical Results associated with Hebei Medical University
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Hebei Medical University
Login to view more data
6,666
Literatures (Medical) associated with Hebei Medical University01 Mar 2026·BEHAVIOURAL BRAIN RESEARCH
Inferring agency: A two-stage process from early integration to late differentiation during action-outcome monitoring
Article
Author: Zhang, Xuemin ; Zhao, Jianxin ; Zou, Xintong ; Chen, Yunyun
Inferring agency-the experience of controlling one's own actions and their consequences-often relies on integrating cues from multiple sources, and recent studies have highlighted the importance of considering the temporal dynamics of this integration process. While previous research has examined how the presence or absence of agency (i.e., reliable versus unreliable sensorimotor cues) affects the neural processing of action-outcomes, it remains unclear whether sensorimotor cues influence this processing dynamically or statically, and how these neural changes relate to explicit judgments of agency. In the present study, participants performed a task in which they moved a ball to a target position under varying motion fluency conditions and then received social feedback regarding their performance, followed by an agency judgement task. Electroencephalography was recorded to capture neural responses during feedback processing. Analyses revealed a dynamic interaction between motion fluency and feedback valence on both the feedback-related negativity (FRN) and explicit agency ratings. Under disfluent motion, the influence of social feedback on both neural responses and agency ratings intensified over time. In contrast, under fluent motion, the influence of social feedback diminished over time. Additionally, FRN was associated with the integration of fluency and feedback, whereas the later P3 component was primarily associated with the influence of fluency on agency ratings. These results indicated that the reflective agency during outcome monitoring could involve an early integration and later differentiation of cues, with the early phase integrating both the sensorimotor and external cues, and the later phase focusing on a more in-depth processing of sensorimotor cues.
01 Feb 2026·Forensic Science International-Genetics
Development and validation of a capture sequencing panel containing 9000 SNPs for inferring distant relatives in East Asian populations
Article
Author: Zeng, Kuo ; Li, Caixia ; Li, Jing ; Fang, Zhixiao ; Zhao, Wenting ; Liu, Jing ; Zhao, Dong ; Zhu, Bofeng
Inferring distant relatives has long presented a significant challenge in forensic science. Recently, forensic researchers have increasingly focused on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as a potent tool for this purpose. In this study, we developed and validated a capture sequencing panel comprising 9000 SNPs specifically aimed at inferring distant relatives within East Asian populations. Initially, we screened the 9000 SNPs from four data sources: the Infinium Global Screening Array, the Infinium Chinese Genotyping Array, the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism database, and the 1000 Genomes Project. Subsequently, we established a likelihood ratio (LR)-based algorithm utilizing pedigree genotyping data from Han Chinese populations. Next, we constructed a sequencing method for the 9000 SNPs employing hybridization capture sequencing technology. Finally, the 9000 SNP panel was evaluated following the validation guidelines of the Scientific Working Group on DNA Analysis Methods (SWGDAM), including studies on repeatability, concordance, sensitivity, species specificity, PCR inhibition, DNA degradation, DNA mixture and casework-type samples. The results demonstrated that the 9000 SNPs exhibited considerable genetic polymorphism within East Asian populations, with an average minor allele frequency of 0.4521. The panel of 9000 SNPs was demonstrated to reliably identify relatives up to the 5th degree and certain 6th degree using the GSA SNP array for pedigree genotyping. Furthermore, the 9000 SNP panel yielded robust and reliable genotyping results for trace DNA (1.953 ng), degraded DNA (50 bp), and mixed DNA (19:1 ratio), showing specific species specificity and resistance to PCR inhibition. In conclusion, this study highlights the significant potential of the 9000 SNP panel for inferring distant relatives in East Asian populations, providing a valuable tool for forensic applications. Further validation in a larger sample size is needed to confirm our observations.
01 Feb 2026·Forensic Science International-Genetics
The coupling of methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme with recombinant polymerase amplification and lateral flow dipstick for the detection of (menstrual) blood stains
Article
Author: Liu, Yi ; Wang, Hongzhe ; Liu, Ying ; Tang, Xuan ; Wang, Chudong ; Jia, Hongtao ; Fu, Xiaoyi ; Wen, Dan ; Li, Jienan ; Liang, Bin ; Zha, Lagabaiyila ; Zhao, Xingchun
Blood is a critical and frequently encountered type of evidence at forensic crime scenes. Its detection can provide valuable insights into the nature of a case and help refine investigative focus. The blood test strip is the most commonly used method for blood detection. However, it is prone to false-negative results, especially when detecting trace amounts of blood found at crime scenes, as well as challenging samples, such as those buried in soil, washed with detergents, and aged samples. In this study, we developed an alternative (menstrual) blood detection method based on the blood-specific methylation site (cg04011671). After treatment with a Methylation-Sensitive Restriction Enzyme (MSRE), the DNA is then amplified using Recombinant Polymerase Amplification (RPA), and the amplification is visualized through Lateral Flow Dipstick (LFD). Our results demonstrate that the MSRE-RPA-LFC method exhibits good specificity for body fluids and species. Additionally, this method shows a sensitivity of 125 pg DNA input, indicating its high detection capability for trace samples. Furthermore, this method is compatible with subsequent DNA analysis and demonstrates superior detection performance compared to traditional blood test strips (e.g., FOB test strips). It can effectively detect samples buried in soil for two weeks or longer, samples cleaned with reagents (e.g. hydrogen peroxide or oxygen bleach), and aged samples stored at room temperature for 10, 9, and 6 years. These findings indicate that this method serves as a confirmatory approach for (menstrual) blood identification and is a promising technique for detecting (menstrual) blood in trace and challenging forensic samples.
3
News (Medical) associated with Hebei Medical University31 Oct 2025
SHANGHAI, Oct. 31, 2025 /PRNewswire/ -- Shanghai Zhimeng Biopharma Inc. ( "Zhimeng") announced that its self-developed new-generation potassium channel opener CB03-154 for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) has officially initiated the phase 2/3 clinical trial and completed the first patient first dose at the 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University. Previously (in July 2025), CB03-154 received approval from the China Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) to conduct the ALS phase 2/3 adaptive clinical trial. The CB03-154 has also been granted orphan drug status in the United States in October 2023 for the treatment of ALS.
This phase 2/3 clinical trial is a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with open-label extension. This study is led by Professor Fan Dongsheng from the 3rd Affiliated Hospital of Peking University as the leading investigator nationwide. This study will enroll approximately 240 patients diagnosed with ALS in about 15 centers in China. The disease duration of to be enrolled patients will be within 24 months from the first symptom onset to the screening visit. The primary efficacy endpoint of the study is the change from baseline at week 39 of the revised ALS Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R) score.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive and fatal central nervous system disease with unknown etiology. It mainly affects the motor neurons in the cerebral cortex, brainstem, and spinal cord. The pathological features of ALS include the loss of upper and lower motor neuron cell bodies, as well as the degeneration of the corticospinal tract/corticobulbar tract and axons of lower motor neurons, and the occurrence of denervation changes in muscles. Clinically, it mainly presents as progressive skeletal muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculation, bulbar palsy, and pyramidal tract signs. The median survival duration is generally 2 to 3 years after the onset of symptoms. The main cause of death is neuromuscular respiratory failure. The annual incidence of ALS in Europe and the United States is 2/100,000 to 3/100,000, and the prevalence rate is 3-5/100,000. The peak age of onset is 50 to 75 years. Approximately 10% of ALS patients are familial, while the remaining 90% are sporadic. Currently, there are no treatments that can stop or reverse the progression of the disease. Therefore, clinical management focuses on early diagnosis and early treatment to maximize the survival time. Currently, only three drugs have been approved worldwide for ALS, namely Riluzole, Edaravone, and Tofersen (trade name Qalsody). These approved drugs can only slightly improve the patient's function or slightly prolong the survival time. Therefore, ALS still has a huge unmet medical need.
Although the pathogenesis of ALS has not been fully deciphered, studies have found that it is closely related to changes in ion channels, synaptic transmission and connections, as well as the imbalance of excitation and inhibition of neurons. Among them, the potassium ion (K+) channel is the most widely distributed and has the largest variety, mainly participating in regulating the excitability of neurons and the frequency and amplitude of action potential generation. Currently, there are no marketed KCNQ2/3 potassium ion channel openers available for ALS patients. The only KCNQ2/3 potassium ion channel opener that was approved by the FDA and EMA, ritigabine (Potiga, Ezogabine/Retigabine), was once studied in ALS patients and showed a favorable signal. However, due to the risks of pigmentation-induced vision impairment and other risk factors, it was withdrawn from the market in 2017.
CB03-154 is a new generation selective voltage-gated potassium channel (KCNQ2/3) opener, independently developed by Zhimeng. Compared with the first-generation potassium channel opener ritigabine, CB03-154 has superior selectivity and stability. In vitro studies have confirmed that CB03-154 can significantly reduce the excessive excitation of iPSC motor neurons from ALS patients. Moreover, in the SOD-1 ALS transgenic mouse model, daily oral administration of CB03-154 (10 mg/kg) can effectively prolong the survival time, delay the onset, improve motor ability, alleviate neuronal damage, and slow down the rate of muscle atrophy.
The initiation of this Phase 2/3 clinical trial is a significant step for CB03-154 in the field of rare diseases, and it brought hopes to provide an important new treatment option for ALS patients.
About Zhimeng
Founded in 2018, Shanghai Zhimeng Biopharma, Inc. is a biopharmaceutical company dedicated to develop small-molecule drug discovery with focused on the functional cure of chronic hepatitis B (CHB), as well as novel therapies for CNS disorders, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain (e.g. cancer-related pain), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), major depressive disorder (MDD), and bipolar disorder.
Disclaimer
This press release contains forward-looking statements. While Zhimeng considers the projections to be based on reasonable assumptions, these forward-looking statements may be called into question by a number of hazards and uncertainties, so that actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in such forward-looking statements.
For more information, please visit:
SOURCE Shanghai Zhimeng Biopharma Inc.
WANT YOUR COMPANY'S NEWS FEATURED ON PRNEWSWIRE.COM?
440k+
Newsrooms &
Influencers
9k+
Digital Media
Outlets
270k+
Journalists
Opted In
GET STARTED
Orphan DrugDrug ApprovalClinical Study
19 Jul 2025
GA, UNITED STATES, July 19, 2025 /
EINPresswire.com
/ -- A growing body of research is revealing the hidden influence of microbes on cancer. Recently, researchers have identified
Fusobacterium nucleatum
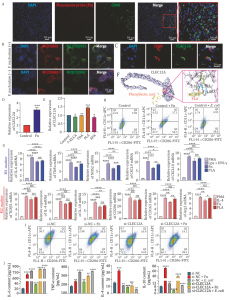
as a key player in shaping the immune environment in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). By integrating data from microbiome, metabolome, and transcriptome analyses, the study shows that the bacterium and an associated metabolite phenyllactic acid (PLA) promote the expression of CLEC12A, an immune receptor that encourages immune-suppressive macrophages. This dual microbial and molecular mechanism may contribute to treatment resistance in some ESCC patients, offering a potential explanation for the uneven response to immunotherapy and a new target for future interventions.
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a deadly cancer with particularly high prevalence in East Asia. While immunotherapy has emerged as a promising treatment, many patients fail to respond—raising questions about hidden factors influencing therapeutic outcomes. Recent studies have turned attention to the tumor microbiome, which can interact with host immunity in complex ways. Oral pathogens such as F. nucleatum, long associated with periodontal disease, are now being implicated in cancer progression and immune escape. Their metabolites may serve as messengers, subtly rewiring the tumor's immune landscape. Due to these challenges, in-depth research is needed to uncover microbial mechanisms that modulate immune responses in ESCC.
In a letter-style study published on October 29, 2024, in Protein & Cell, a research team from the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, etc. revealed how Fusobacterium nucleatum manipulates immune behavior in ESCC. Drawing from a cohort of 52 patient samples, the team conducted microbiome sequencing, transcriptome analysis, and metabolomics profiling. Their work uncovered a strong link between microbial colonization, immune receptor expression, and immune cell polarization—offering fresh insight into how bacteria might undercut the body's cancer-fighting abilities.
The researchers divided ESCC patients into treated and untreated groups and profiled their tumors at multiple molecular levels. They found that F. nucleatum was significantly more abundant in untreated tumors and was associated with more advanced cancer stages. Transcriptome analysis revealed that patients with high levels of this bacterium also had increased expression of CLEC12A, a receptor found on immune cells like macrophages. These immune cells, when influenced by F. nucleatum, shifted toward the M2 state—a pro-tumor phenotype characterized by heightened expression of immunosuppressive markers (e.g., CD206, CD163).
Further analysis pointed to phenyllactic acid (PLA), a metabolite associated with the bacterium, as a key driver of this effect. Lab experiments confirmed that both F. nucleatum and PLA upregulated CLEC12A and boosted M2 macrophage markers in cultured immune cells. Silencing CLEC12A reduced the bacterium's effect on M2 polarization and restored pro-inflammatory responses. These findings suggest a microbiota-driven mechanism that helps tumors escape immune surveillance by recruiting "tolerant" immune cells, and they highlight CLEC12A as a potential molecular bridge between microbial signals and immune modulation.
This study shines a light on the microbial dark matter of cancer, said Dr. Jing Zuo, one of the co-corresponding authors of the study. The research team has uncovered how F. nucleatum not only survives in tumor environments but actively changes how immune cells behave. By producing or associating with specific metabolites like PLA, the bacterium effectively reprograms macrophages into a tumor-supportive state. This opens up exciting possibilities for developing precision immunotherapy that takes a patient's microbiome into account.
The findings open new frontiers in the battle against ESCC. With F. nucleatum and PLA shown to influence immune evasion, the study points to microbiome profiling as a potential predictive tool for immunotherapy success. Therapies that disrupt this microbial-immunological axis—such as targeting CLEC12A or modifying gut flora—could offer innovative ways to overcome treatment resistance. Additionally, these insights could extend beyond ESCC, prompting researchers to investigate similar microbial effects in other cancers. As the interplay between microbes and immunity becomes clearer, the future of cancer therapy may hinge on more than just genetics—it may depend on our microbial cohabitants as well.
References
DOI
10.1093/procel/pwae063
Original Source URL
https://doi-org.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/10.1093/procel/pwae063
Funding information
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82373072) awarded to Z.N., the Key Project of Hebei Province Natural Science Precision Medicine Joint Fund (H2022201067) awarded to Z.N., and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. H2024206159) awarded to J.Z.
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability
for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this
article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
ImmunotherapyClinical Study
09 Jun 2025
ROCKVILLE, Md. and SUZHOU, China, June 09, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Ascentage Pharma (NASDAQ: AAPG; HKEX: 6855), a global biopharmaceutical company dedicated to addressing unmet medical needs in cancers, announced that 13 studies of its core assets - including the novel drug olverembatinib (HQP1351), the investigational Bcl-2 inhibitor lisaftoclax (APG-2575), and the investigational EED inhibitor APG-5918 – will be featured in an oral presentation, multiple poster presentations and multiple online publications at the 2025 European Hematology Association (EHA) Annual Congress taking place in Milan, Italy, from June 12-15, 2025.
The EHA Annual Congress is the largest gathering of the hematology community in Europe. Attracting more than 10,000 attendees from more than 100 countries every year, the congress showcases cutting-edge research and ground-breaking clinical results in the field of hematology.
Oral Presentation
Integrating Genomic and Transcriptomic Insights for Predicting Responses and Outcomes in Patients with CML Receiving 3rd-Generation TKI Therapy
Abstract#: S162
Session: Biology of CML treatment response and resistance
Date and Time: Saturday, 14 June, 17:30-17:45 CEST / Saturday, 14 June, 23:30-23:45 Beijing Time
Principal Authors: Prof. Qian Jiang, Peking University People’s Hospital; Dr. Xiaoshuai Zhang, Peking University People’s Hospital
Poster Presentations
Frontline Chemotherapy-Free Combination of Olverembatinib with Venetoclax and Azacitidine in Newly Diagnosed Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Preliminary Outcomes of a Prospective Study
Abstract#: PF384
Session: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Clinical
Date and Time: Friday, 13 June, 18:30-19:30 CEST / Saturday, 14 June, 00:30-01:30 Beijing Time
Principal Author: Prof. Xiaowen Tang, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University; Xin Zhang, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University
A Phase 2 Study of Olverembatinib for the Treatment of Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms with FGFR1 Rearrangement
Abstract#: PF390
Session: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Clinical
Date and Time: Friday, 13 June, 18:30-19:30 CEST / Saturday, 14 June, 00:30-01:30 Beijing Time
Principal Authors: Prof. Suning Chen, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University; Wenzhi Cai, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University
Efficacy and Safety of Regimen with Olverembatinib and Blinatumomab for the Frontline Treatment of Ph-Positive or Ph-Like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract#: PS1367
Session: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Clinical
Date and Time: Saturday, 14 June, 18:30-19:30 CEST / Sunday, 15 June, 00:30-01:30 Beijing Time
Principal Authors: Prof. Hongsheng Zhou, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University; Xiuli Xu, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University
Combination of Olverembatinib and VP Regimen as First-Line Therapy for Adult Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial
Abstract#: PS1372
Session: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Clinical
Date and Time: Saturday, 14 June, 18:30-19:30 CEST / Sunday, 15 June, 00:30-01:30 Beijing Time
Principal Authors: Prof. Jie Jin, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine; Dr. Gaixiang Xu, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Efficacy and Safety of The Third-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Olverembatinib in Combination with Inotuzumab Ozogamicin for the Treatment of Adult Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients With Relapsed Disease or Persistent Minimal Residual Disease Bridging to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Phase II Study
Abstract#: PS1387
Session: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia – Clinical
Date and Time: Saturday, 14 June, 18:30-19:30 CEST / Sunday, 15 June, 00:30-01:30 Beijing Time
Principal Author: Erlie Jiang, Institute of Hematology & Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College; Xiaoyu Zhang, Institute of Hematology & Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College
Embryonic Ectoderm Development (EED) Inhibitor APG-5918 Exhibits Potent Antitumor Activity and Synergizes with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Tucidinostat in Preclinical
T-Cell Lymphoma (TCL) Models
Abstract#: PS1993
Session: Lymphoma biology & translational research
Date and Time: Saturday, 14 June, 18:30-19:30 CEST / Sunday, 15 June, 00:30-01:30
Principal Author: Dr. Eric Liang, Ascentage Pharma Group Inc.
Online Publications
Alternating Low-Dose Inotuzumab Ozogamicin and Blinatumomab in Maintenance Therapy for Ph+ ALL: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis
Abstract: PB2384
Principal Author: Prof. Zi-Yuan Nie, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University
Efficacy and Safety of Blinatumomab in Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Ph-Positive/Negative B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract#: PB2363
Principal Author: Yinqiang Zhang, Institute of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Efficacy and Safety of the Third-Generation TKI Olverembatinib in Relapsed and Persistent MRD Positive Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients
Abstract#: PB2360
Principal Author: Xinwen Jiang, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University
Clinical Features and Genetic Abnormalities Predict Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the Accelerated-Phase Receiving Olverembatinib Therapy: A Retrospective Multicenter Study
Abstract#: PB2701
Principal Author: Mengyao Yuan, Peking University People's Hospital
A Real-World Study of Olverembatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia from China: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
Abstract#: PB2714
Principal Author: Tian Dong, West China Hospital of Sichuan University
Synergistic Effects of Olverembatinib (HQP1351) Combined with Bcl-2 Inhibitor Lisaftoclax (APG-2575) and Bcl-2/Bcl-xL Inhibitor Pelcitoclax (APG-1252) in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL)
Abstract#: PB2341
Principal Author: Bo Peng, Ascentage Pharma (Suzhou) Co., Ltd.
About Ascentage Pharma
Ascentage Pharma (NASDAQ: AAPG; HKEX: 6855) is a global biopharmaceutical company dedicated to addressing unmet medical needs in cancers. The company has built a rich pipeline of innovative drug candidates that includes inhibitors targeting key proteins in the apoptotic pathway, such as Bcl-2 and MDM2-p53 and next-generation kinase inhibitors.
The lead asset, olverembatinib, is the first novel third-generation BCR-ABL1 inhibitor approved in China for the treatment of patients with CML in chronic phase (CML-CP) with T315I mutations, CML in accelerated phase (CML-AP) with T315I mutations, and CML-CP that is resistant or intolerant to first and second-generation TKIs. It is covered by the China National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL). The Company is currently conducting an FDA-cleared, global registrational Phase III trial, or POLARIS-2, of olverembatinib for CML, as well as global registrational Phase III trials for newly diagnosed Ph
+
ALL patients and SDH-deficient GIST patients.
The second lead asset, lisaftoclax, is a novel Bcl-2 inhibitor for the treatment of various hematologic malignancies. The NDA for the treatment of relapsed and/or refractory CLL and SLL was accepted with Priority Review designation by China’s National Medical Products Administration. The Company is currently conducting an FDA-cleared, global registrational Phase III trial, or GLORA, of lisaftoclax in combination with BTK inhibitors for patients with CLL/SLL previously treated with BTK inhibitors for more than 12 months with suboptimal response, as well as global registrational Phase III trials for newly diagnosed CLL/SLL, AML, and MDS patients.
Leveraging its robust R&D capabilities, Ascentage Pharma has built a portfolio of global intellectual property rights and entered into global partnerships and other relationships with numerous leading biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, such as Takeda, AstraZeneca, Merck, Pfizer, and Innovent, in addition to research and development relationships with leading research institutions, such as Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Mayo Clinic, National Cancer Institute and the University of Michigan. For more information, visit
https://ascentage.com/
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release includes forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. All statements, other than statements of historical facts, contained in this press release may be forward-looking statements, including statements that express Ascentage Pharma’s opinions, expectations, beliefs, plans, objectives, assumptions or projections regarding future events or future results of operations or financial condition. These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties as discussed in Ascentage Pharma’s filings with the SEC, including those set forth in the sections titled “Risk factors” and “Special note regarding forward-looking statements and industry data” in its Registration Statement on Form F-1, as amended, filed with the SEC on January 21, 2025, and the Form 20-F filed with the SEC on April 16, 2025, the sections headed “Forward-looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” in the prospectus of the Company for its Hong Kong initial public offering dated October 16, 2019, and other filings with the SEC and/or The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited we made or make from time to time that may cause actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements to be materially different from the information expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements contained in this presentation do not constitute profit forecast by the Company’s management.
As a result of these factors, you should not rely on these forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. The forward-looking statements contained in this press release are based on Ascentage Pharma’s current expectations and beliefs concerning future developments and their potential effects and speak only as of the date of such statements. Ascentage Pharma does not undertake any obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Contacts
Investor Relations:
Hogan Wan, Head of IR and Strategy
Ascentage Pharma
Hogan.Wan@ascentage.com
+86 512 85557777
Stephanie Carrington
ICR Healthcare
Stephanie.Carrington@icrhealthcare.com
+1 (646) 277-1282
Media Relations:
Sean Leous
ICR Healthcare
Sean.Leous@icrhealthcare.com
+1 (646) 866-4012
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability
for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this
article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.

Phase 2Phase 3Priority ReviewNDA
100 Deals associated with Hebei Medical University
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with Hebei Medical University
Login to view more data
Corporation Tree
Boost your research with our corporation tree data.
login
or

Pipeline
Pipeline Snapshot as of 24 Feb 2026
The statistics for drugs in the Pipeline is the current organization and its subsidiaries are counted as organizations,Early Phase 1 is incorporated into Phase 1, Phase 1/2 is incorporated into phase 2, and phase 2/3 is incorporated into phase 3
Discovery
11
12
Preclinical
Phase 2
1
1
Other
Login to view more data
Current Projects
| Drug(Targets) | Indications | Global Highest Phase |
|---|---|---|
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells(Hebei Medical University) | COVID-19 More | Phase 1/2 |
HUC-MSCs-Exos (The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University) | Osteoarthritis More | Clinical |
MM@R-β-tCh NPs | Atherosclerosis More | Preclinical |
Notoginsenoside R1 ( HK2 x LDHA x PFKL ) | Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension More | Preclinical |
Beta-hydroxybutyrate ( 5-HT receptor x CLDN1 x HSP70 heat-shock proteins ) | Neuroinflammation More | Preclinical |
Login to view more data
Deal
Boost your decision using our deal data.
login
or

Translational Medicine
Boost your research with our translational medicine data.
login
or

Profit
Explore the financial positions of over 360K organizations with Synapse.
login
or

Grant & Funding(NIH)
Access more than 2 million grant and funding information to elevate your research journey.
login
or

Investment
Gain insights on the latest company investments from start-ups to established corporations.
login
or

Financing
Unearth financing trends to validate and advance investment opportunities.
login
or

AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free


