Request Demo
Last update 18 Nov 2025

bluebird bio, Inc.
Last update 18 Nov 2025
Overview
Tags
Hemic and Lymphatic Diseases
Other Diseases
Congenital Disorders
Gene therapy
Hematopoietic stem cell therapy
CAR-T
Disease domain score
A glimpse into the focused therapeutic areas
No Data
Technology Platform
Most used technologies in drug development
No Data
Targets
Most frequently developed targets
No Data
| Top 5 Drug Type | Count |
|---|---|
| Gene therapy | 5 |
| CAR-T | 2 |
| Autologous CAR-T | 1 |
| Stem cell therapy | 1 |
| TCR-T Cell therapy | 1 |
Related
11
Drugs associated with bluebird bio, Inc.Target |
Mechanism β-globin stimulants |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc. United States |
First Approval Date08 Dec 2023 |
Target |
Mechanism ABCD1 gene stimulants |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication- |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc. European Union [+3] |
First Approval Date16 Jul 2021 |
20
Clinical Trials associated with bluebird bio, Inc.NCT06224413
A Postmarketing, Prospective, Multicenter, Observational, Long-Term Safety and Effectiveness Registry Study of Patients With Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD) Treated With Elivaldogene Autotemcel (Stargazer)
The main aim of this study is to assess and describe the safety outcomes, including newly diagnosed malignancies, of patients with CALD treated with eli-cel in the post-marketing setting (tradename Skysona) and to describe major functional disability (MFD)-free survival over time in participants with more advanced early active CALD. All enrolled participants with CALD treated with eli-cel in the post-marketing setting will be followed in this study for 15 years. No investigational drug product will be administered in this study. This study will enroll 120 participants with CALD treated with eli-cel in the post-marketing setting. A subpopulation of 24 participants with more advanced early active CALD will be specifically enrolled as required by the US FDA as a condition of accelerated approval and will be considered as a separate cohort for effectiveness outcomes.
Start Date27 Mar 2024 |
Sponsor / Collaborator  bluebird bio, Inc. bluebird bio, Inc. [+1] |
NCT06271512
A Safety and Effectiveness Registry Study of Patients with Β-Thalassemia Treated with Betibeglogene Autotemcel (the Glostar Registry)
The main aim of this study is to collect real-world longitudinal data on participants with β-thalassemia treated with betibeglogene autotemcel (beti-cel) in the post marketing setting. To assess the long-term safety, including the risk of newly diagnosed malignancies, after treatment with beti-cel and evaluate the long-term effectiveness of treatment with beti-cel.
Start Date23 Jan 2024 |
Sponsor / Collaborator  bluebird bio, Inc. bluebird bio, Inc. [+1] |
NCT05353647
A Multi-Center, Phase 2 Gene Transfer Study Inducing Fetal Hemoglobin in Sickle Cell (GRASP, BMT CTN 2001)
A promising approach for the treatment of genetic diseases is called gene therapy. Gene therapy is a relatively new field of medicine in which genetic material (mostly DNA) in the patient is changed to treat his or her own disease. In gene therapy, we introduce new genetic material in order to fix or replace the patient's disease gene, with the goal of curing the disease. The procedure is similar to a bone marrow transplant, in that the patient's malfunctioning blood stem cells are reduced or eliminated using chemotherapy, but it is different because instead of using a different person's (donor) blood stem cells for the transplant, the patient's own blood stem cells are given back after the new genetic material has been introduced into those cells. This approach has the advantage of eliminating any risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD), reducing the risk of graft rejection, and may also allow less chemotherapy to be utilized for the conditioning portion of the transplant procedure. To introduce new genetic material into the patient's own blood stem cells we use a modified version of a virus (called a 'vector') that efficiently inserts the "correcting" genetic material into the cells. The vector is a specialized biological medicine that has been formulated for use in human beings.
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) is a healthy, non-sickling kind of hemoglobin. The investigators have discovered a gene that is very important in controlling the amount of HbF. Decreasing the expression of this gene in sickle cell patients could increase the amount of fetal hemoglobin while simultaneously reducing the amount of sickle hemoglobin in their blood, specifically the amount in red blood cells where sickle hemoglobin causes damage to the cell, and therefore potentially cure or significantly improve the condition. The gene we are targeting for change in this study that controls the level of fetal hemoglobin is called BCL11A.
In summary, the advantages of a gene therapy approach include: 1) it can be used even if the patient does not have a matched donor available; 2) it may allow a reduction in the amount of chemotherapy required to prepare the patient for the transplant; and 3) it will avoid certain strong medicines often required to prevent and treat GVHD and rejection. Our lab studies with normal mice, mice that have a form of SCD, and with cells from the bone marrow of SCD patients who have donated bone marrow for research purposes show this approach is very effective in reducing the amount of sickle hemoglobin in red cells. Our pilot trial testing this approach in 10 patients with SCD has shown that the treatment has not caused any unexpected safety problems, and that it increases HbF within the red blood cells. Our goal is to continue to test whether this approach is safe, and whether using gene therapy to change the expression of BCL11A will lead to decreased episodes of vaso-occlusive crisis pain in people with SCD.
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) is a healthy, non-sickling kind of hemoglobin. The investigators have discovered a gene that is very important in controlling the amount of HbF. Decreasing the expression of this gene in sickle cell patients could increase the amount of fetal hemoglobin while simultaneously reducing the amount of sickle hemoglobin in their blood, specifically the amount in red blood cells where sickle hemoglobin causes damage to the cell, and therefore potentially cure or significantly improve the condition. The gene we are targeting for change in this study that controls the level of fetal hemoglobin is called BCL11A.
In summary, the advantages of a gene therapy approach include: 1) it can be used even if the patient does not have a matched donor available; 2) it may allow a reduction in the amount of chemotherapy required to prepare the patient for the transplant; and 3) it will avoid certain strong medicines often required to prevent and treat GVHD and rejection. Our lab studies with normal mice, mice that have a form of SCD, and with cells from the bone marrow of SCD patients who have donated bone marrow for research purposes show this approach is very effective in reducing the amount of sickle hemoglobin in red cells. Our pilot trial testing this approach in 10 patients with SCD has shown that the treatment has not caused any unexpected safety problems, and that it increases HbF within the red blood cells. Our goal is to continue to test whether this approach is safe, and whether using gene therapy to change the expression of BCL11A will lead to decreased episodes of vaso-occlusive crisis pain in people with SCD.
Start Date12 Jul 2022 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
100 Clinical Results associated with bluebird bio, Inc.
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with bluebird bio, Inc.
Login to view more data
41
Literatures (Medical) associated with bluebird bio, Inc.14 Jan 2025·Blood Advances
Gene therapy in transfusion-dependent non-β0/β0 genotype β-thalassemia: first real-world experience of beti-cel
Article
Author: Heine, Sabine ; Kunz, Joachim ; Thakar, Himal ; Schmitt, Michael ; Laier, Sascha ; Jakoby, Donate ; Koscher, Leila ; Greil, Johann ; Kulozik, Andreas ; Ritsert, Mona-Lisa ; Mirza, Adil ; Tao, Gloria ; Pavel, Petra ; Lobitz, Stephan ; Dürken, Matthias ; Schmitt, Anita
Abstract:
Gene addition and editing strategies for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia have gained momentum as potentially curative treatment options, with studies showcasing their efficacy and safety. We report, to our knowledge, the first real-world application of betibeglogene autotemcel (beti-cel; Zynteglo) during its period of active license in Europe from January 2020 to March 2022 for patients aged ≥12 years without a β0/β0 genotype and without a HLA-matched sibling donor, before beti-cel marketing authorization was withdrawn by its holder because of nonsafety reasons. Among 15 screened patients, 4 opted out for fertility and safety concerns, 2 were excluded because of marked hepatic siderosis, and 1 had apheresis collection failure. Eight patients received beti-cel after busulfan myeloablative conditioning, all achieving transfusion independence within 8 to 59 days, with posttreatment hemoglobin levels ranging from 11.3 to 19.3 g/dL. No deaths occurred, but acute toxicity mirrored busulfan’s known effects. Posttreatment platelet management faced challenges because of HLA-antibodies in 3 patients. Monitoring up to month 24 revealed pituitary-gonadal endocrine dysfunction in all 3 female and in 2 of 5 male patients. Additionally, we observed unexpected posttreatment sequelae: 1 patient developed polycythemia that could not be explained by known genetic or acquired mechanisms, 1 patient developed posttreatment depression and anxiety prohibiting her from returning to work, and 1 patient developed fatigue severely compromising both quality of life and work capacity. This real-world experience corroborates beti-cel’s efficacy and safety and provides information on adverse events observed during real-world use of the therapy.
09 Apr 2024·Blood advances
In vivo measurement of RBC survival in patients with sickle cell disease before or after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Article
Author: Tisdale, John F. ; Thein, Swee Lay ; Leonard, Alexis K. ; Hsieh, Matthew M. ; Pierciey, Francis J. ; VanNest, Sara ; Gudmundsdottir, Bjorg ; Eaton, William A. ; DiNicola, Julia ; Hinds, Malikiya ; Wang, Xunde ; Bonner, Melissa ; Demirci, Selami ; Furstenau, Dana ; Macari, Elizabeth R. ; Essawi, Khaled ; Li, Quan ; Cellmer, Troy ; Inam, Zaina ; Chu, Rebecca ; Luckett, Christina
Abstract:
Stable, mixed-donor–recipient chimerism after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) is sufficient for phenotypic disease reversal, and results from differences in donor/recipient–red blood cell (RBC) survival. Understanding variability and predictors of RBC survival among patients with SCD before and after HSCT is critical for gene therapy research which seeks to generate sufficient corrected hemoglobin to reduce polymerization thereby overcoming the red cell pathology of SCD. This study used biotin labeling of RBCs to determine the lifespan of RBCs in patients with SCD compared with patients who have successfully undergone curative HSCT, participants with sickle cell trait (HbAS), and healthy (HbAA) donors. Twenty participants were included in the analysis (SCD pre-HSCT: N = 6, SCD post-HSCT: N = 5, HbAS: N = 6, and HbAA: N = 3). The average RBC lifespan was significantly shorter for participants with SCD pre-HSCT (64.1 days; range, 35-91) compared with those with SCD post-HSCT (113.4 days; range, 105-119), HbAS (126.0 days; range, 119-147), and HbAA (123.7 days; range, 91-147) (P<.001). RBC lifespan correlated with various hematologic parameters and strongly correlated with the average final fraction of sickled RBCs after deoxygenation (P<.001). No adverse events were attributable to the use of biotin and related procedures. Biotin labeling of RBCs is a safe and feasible methodology to evaluate RBC survival in patients with SCD before and after HSCT. Understanding differences in RBC survival may ultimately guide gene therapy protocols to determine hemoglobin composition required to reverse the SCD phenotype as it relates directly to RBC survival. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT04476277.
01 Dec 2023·Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development
Drug product attributes predict clinical efficacy in betibeglogene autotemcel gene therapy for β-thalassemia
Article
Author: Kral, Kelly ; Whitney, Dustin ; d'Anjou, Marc ; Gayron, Marisa ; Pierciey, Francis J ; Colvin, Richard A ; Fincker, Maeva ; Shestopalov, Ilya
Ex vivo autologous hematopoietic stem cell lentiviral-based gene therapy with betibeglogene autotemcel has been studied in patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia in Phase III clinical trials (HGB-207 and HGB-212), with 90% of patients reaching transfusion independence (TI). Here, we explore manufacturing parameters, drug product quality attributes, and limited patient characteristics that had an impact on clinical efficacy in HGB-207 and HGB-212. Retrospective analysis revealed that the peripheral blood vector copy number (VCN) was related to TI, with a strong correlation between peripheral blood VCN at 6 months and gene therapy-derived therapeutic protein (HbAT87Q) expression at 6 months (correlation coefficient, 0.8681; p < 0.0001; R2 = 0.7536). A peripheral blood VCN threshold of ≥0.75 copies per diploid genome at 6 months post betibeglogene autotemcel infusion provided a stringent surrogate biomarker for TI and was used as the outcome variable for multivariate analysis using a random forest classifier. The top predictive feature of clinical efficacy was found to be the percentage of lentiviral vector-positive cells in the drug product. This retrospective analysis is critical to understanding the key product quality attributes that can predict clinical efficacy in lentiviral vector gene therapy within this clinical trial population.
292
News (Medical) associated with bluebird bio, Inc.05 Sep 2025
Rising prevalence of genetic disorders, supportive regulatory frameworks, and advancements in gene and RNA-based therapies are fueling market expansion.
WILMINGTON, DE, UNITED STATES, September 5, 2025 /
EINPresswire.com
/ -- The global
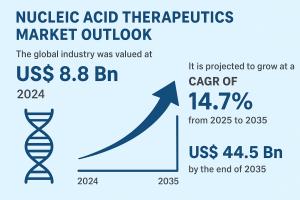
nucleic acid therapeutics market
is entering a phase of accelerated growth, driven by strong innovation pipelines and favorable policy support. Valued at US$ 8.8 Bn in 2024, the market is projected to grow at a robust CAGR of 14.7% between 2025 and 2035, reaching US$ 44.5 Bn by 2035. Growing awareness of genetic diseases, widespread clinical trials, and rapid progress in RNA-based platforms are reshaping the future of precision medicine.
Market Introduction
Nucleic acid therapeutics represent one of the most transformative innovations in modern biotechnology. These therapies leverage engineered DNA and RNA molecules to correct or silence defective genes, introduce beneficial genetic material, or modulate protein expression. Core modalities include gene therapies, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), RNA interference (RNAi), aptamers, and messenger RNA (mRNA)-based therapeutics.
Their therapeutic applications extend across neuromuscular disorders, oncology, viral infections, ophthalmological diseases, metabolic syndromes, and autoimmune conditions, providing high specificity, targeted action, and the potential for one-time curative treatments. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals, nucleic acid therapeutics address the root cause of diseases at the genetic level, minimizing systemic toxicity and enabling personalized medicine.
Dive Deeper into Data: Get Your In-Depth Sample Now -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=S&rep_id=86333
Analyst Viewpoint
Analysts at Transparency Market Research note that the nucleic acid therapeutics market is on the cusp of becoming a mainstream segment in the biopharmaceutical industry.
Key growth catalysts include:
Rising prevalence of rare and inherited disorders such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, and sickle cell anemia, which remain underserved by conventional treatments.
Regulatory acceleration through FDA Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy, and EMA Priority Medicines (PRIME) designations, which shorten development timelines for critical therapies.
Challenges remain in terms of manufacturing scalability, delivery mechanisms, and cost-effectiveness, particularly for therapies requiring complex viral or lipid nanoparticle vectors. However, the success of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has proven the scalability and adaptability of RNA-based platforms, catalyzing confidence among investors and policymakers. The increasing number of clinical trials, coupled with strategic collaborations, points to a market that is set to transform global healthcare by 2035.
Key Market Drivers
1. Rising Prevalence of Genetic Disorders
Genetic diseases affect millions worldwide, with a growing number being diagnosed through advancements in genomic sequencing and prenatal screening. This improved detection rate is expanding the eligible patient pool for nucleic acid therapeutics. As these therapies directly correct or silence defective genes, their adoption is expected to increase significantly in the coming years.
2. Regulatory Approvals and Expedited Pathways
Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are creating streamlined approval frameworks for nucleic acid therapeutics, particularly in the area of rare and orphan diseases. Expedited review processes reduce time-to-market, encouraging pharmaceutical and biotech companies to increase investment in clinical development.
3. Advancements in RNA-based and Gene Therapies
Breakthroughs in antisense oligonucleotides, siRNA, and mRNA platforms are enabling therapies that target diseases previously considered untreatable. The integration of artificial intelligence, nanotechnology-driven delivery systems, and improved chemical modifications has enhanced drug stability, precision targeting, and reduced off-target effects, making RNA-based treatments commercially viable.
Segment Analysis
By Therapy Type
Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs): Largest segment due to their efficacy in modulating gene expression; widely used in neuromuscular and rare genetic disorders.
Small Interfering RNA (siRNA): Emerging as a strong segment with applications in oncology and metabolic diseases.
Gene Therapies: High growth potential owing to curative benefits in monogenic disorders.
Aptamers: Gaining momentum in targeted oncology treatments.
Others (including mRNA therapies): Strong future growth expected, particularly post-COVID-19 success.
By Delivery Method
Viral Vector-based Systems: Widely used but face challenges in immunogenicity and manufacturing scalability.
Non-viral Delivery Systems: Lipid nanoparticles and polymer-based carriers showing promising safety and efficiency.
By Route of Administration
Intravenous: Dominant due to systemic distribution.
Subcutaneous: Preferred for ease of administration and chronic therapies.
Others (Intrathecal, etc.): Specialized routes for targeted disease conditions.
By Therapeutic Area
Neuromuscular Disorders (DMD, SMA)
Metabolic Disorders
Cardiovascular Disorders
Ophthalmological Disorders
Oncological Disorders
Others (Infectious, Autoimmune, etc.)
By End-user
Hospitals (largest share due to advanced care infrastructure)
Academic and Research Institutes (driving clinical trials and innovation)
Specialty Centers (focusing on genetic and rare disorders)
Regional Insights
North America: Leads the global market due to strong biotech infrastructure, presence of leading companies, and early adoption of innovative therapies. Favorable reimbursement policies and active regulatory support enhance growth prospects.
Europe: Rapid adoption supported by EMA’s proactive stance on genetic therapies. Strong research ecosystems in Germany, the UK, and France are advancing innovation.
Asia Pacific: Poised for fastest growth with rising healthcare investments, supportive government initiatives, and a growing patient pool in China, India, and Japan.
Latin America & Middle East & Africa: Emerging regions where adoption is gradually increasing, though affordability and access remain challenges. Partnerships with global biotech firms are expected to enhance growth.
Key Players
Novartis AG
Pfizer, Inc.
Sanofi
Novo Nordisk A/S
AstraZeneca plc
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Amgen Inc.
Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.
Bluebird Bio, Inc.
CSL Behring LLC
Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Krystal Biotech, Inc.
PTC Therapeutics, Inc.
Jazz Pharmaceuticals plc
Astellas Pharma Inc.
Recent Developments
Novartis (Nov 2024): Acquired Kate Therapeutics, expanding its AAV-based gene therapy pipeline for neuromuscular diseases in a deal valued up to US$ 1.1 Bn.
Sarepta Therapeutics (Nov 2024): Entered into a licensing agreement with Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals for siRNA programs in muscle and rare pulmonary disorders, valued at US$ 825 Mn.
Market Trends
Accelerating investments in RNA-based and gene-editing platforms.
Rising demand for personalized and precision medicine approaches.
Continuous technological innovations in viral and non-viral delivery platforms.
Increasing collaborations between pharma companies, biotech firms, and academic institutions to fast-track clinical pipelines.
Future Outlook
The nucleic acid therapeutics market is expected to remain one of the fastest-growing sectors within biotechnology and pharmaceuticals through 2035.
Factors such as increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, regulatory acceleration, advancements in RNA and gene therapy platforms, and strong demand for personalized medicine will drive market expansion. With a projected CAGR of 14.7%, the sector is set to deliver groundbreaking treatments that could redefine modern healthcare.
Why Buy This Report?
Reliable market size forecasts and CAGR projections through 2035
In-depth assessment of market drivers, restraints, and opportunities
Comprehensive segmentation by therapy type, delivery method, therapeutic area, and region
Competitive landscape with profiles of leading companies and recent strategic developments
Analysis of emerging technologies and trends shaping future growth
Browse More Trending Research Reports:
Nucleic Acid Extraction Instruments & Reagents Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/nucleic-acid-extraction-instruments-reagents-market.html
Oligonucleotide Synthesis Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/oligonucleotide-synthesis-market.html
Aptamers Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/aptamers-market.html
RNA Therapeutics Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/rna-therapeutics-market.html
Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Therapeutics Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/small-interfering-rna-therapeutics-market-report.html
Dark Genome Therapeutics Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/dark-genome-therapeutics-market.html
Nucleic Acid Aptamers Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/nucleic-acid-aptamers.html
Ligase Enzymes Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/ligase-enzymes-market.html
Thermal Cycler Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/thermal-cycler-market.html
Electroporation Instruments Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/electroporation-instruments-market.html
Legionella Testing Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/legionella-testing-market.html
Cell Analysis Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/cell-analysis-market.html
Molecular Diagnostics Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/molecular-diagnostics-industry.html
Biobanking Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/biobanking-market.html
Genetic Testing Services Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/genetic-testing-services-market.html
Array Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/global-array-market.html
Oligonucleotides Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/oligonucleotides-market.html
Digital PCR & Quantitative PCR Market -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/digital-pcr-quantitative-pcr-market.html
About Transparency Market Research
Transparency Market Research, a global market research company registered at Wilmington, Delaware, United States, provides custom research and consulting services. Our exclusive blend of quantitative forecasting and trends analysis provides forward-looking insights for thousands of decision makers. Our experienced team of Analysts, Researchers, and Consultants use proprietary data sources and various tools & techniques to gather and analyses information.
Our data repository is continuously updated and revised by a team of research experts, so that it always reflects the latest trends and information. With a broad research and analysis capability, Transparency Market Research employs rigorous primary and secondary research techniques in developing distinctive data sets and research material for business reports.
Contact:
Transparency Market Research Inc.
CORPORATE HEADQUARTER DOWNTOWN,
1000 N. West Street,
Suite 1200, Wilmington, Delaware 19801 USA
Tel: +1-518-618-1030
USA – Canada Toll Free: 866-552-3453
Website:
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com
Email: sales@transparencymarketresearch.com
Follow Us: LinkedIn| Twitter| Blog | YouTube
Atil Chaudhari
Transparency Market Research Inc.
+1 518-618-1030
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability
for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this
article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
AcquisitionLicense out/inOligonucleotide
20 Aug 2025
Dive Brief:Rocket Pharmaceuticals plans to restart a Phase 2 gene therapy trial for a rare heart disease after working with the Food and Drug Administration to resolve questions around a study participants death earlier this year.The FDA ordered a hold on the research in May after the patient suffered from capillary leak syndrome, a condition characterized by plasma and protein seeping from blood vessels into surrounding tissue. At the time, Rocket zeroed in on a new medicine it had added into the pre-treatment regimen as a possible cause of the deadly complication.Rocket said Wednesday that the FDA lifted its hold and allowed the study to proceed with a lower dose of the companys RP-A501 gene therapy and the discontinuation of the added medicine, called a C3 complement inhibitor. Rocket shares jumped by as much as 40% in early trading Wednesday before falling back.Dive Insight:The end of the clinical hold is good news for the company. But Rocket still has a long way to go to win approval of what could be the first gene therapy for a cardiovascular condition. Analysts said they will be particularly focused on the efficacy of the lower dose, the impact of the new pre-treatment regimen and whether the FDA will demand any more changes to the study as it progresses.Rocket was one of the industrys highest-profile companies four years ago; its shares traded above $64 and its market value topped that of then more well-established competitors, including Bluebird bio and Sangamo Therapeutics. But an unexpected clinical hold in 2021 due to FDA demands for additional risk mitigation methods and the patients death this year caused Rocket shares to crater.The end of the latest clinical hold is a meaningful positive for the stock, Leerink Partners analyst Mani Foroohar wrote in a note to clients Wednesday. The Phase 1 data suggest that a lower dose could be effective enough to win approval to treat Danon disease and puts the heart condition back on the table as a central pillar of the story, with a possible launch in 2029, he wrote.Currently, the only available treatment for Danon disease is a heart transplant. The condition affects between 15,000 and 30,000 patients in the U.S. and Europe, Rocket said.Rocket highlighted the fact that the FDAs clinical hold was resolved in less than three months. That could be a good sign that the head of the agencys biologics division, Vinay Prasad, is fostering a collaborative and understanding unit, Jefferies analyst Andrew Tsai wrote in a note to clients. '
Gene TherapyPhase 1
16 Aug 2025
Bengaluru: In the latest setback for
Pfizer
's
sickle cell anemia
treatments, experimental drug
inclacumab
failed to meet the main goal in a late-stage trial for patients aged 16 and older.
The trial results showed no significant difference in the number of vaso-occlusive crises - or painful events common in sickle cell disease - among people who took the drug versus those who took the placebo, the drugmaker said on Friday.
This makes inclacumab the second drug from Pfizer's 2022 acquisition of
Global Blood Therapeutics
to yield unfavorable results.
Oxbryta
- the centerpiece of the $5.4 billion buyout - was withdrawn last September over risks of painful complications and deaths.
"Pfizer's acquisition of Global Blood has proven disappointing with inclacumab's failure coming after Oxbryta's 2024 withdrawal from all approved markets" said
BMO Capital Markets
analyst Evan Seigerman.
The previously estimated $3 billion in revenue contributions from the deal now seems unlikely to materialize, Seigerman said.
Pfizer said it was disappointed by inclacumab's results but remains committed to supporting the sickle cell community.
The company will keep working on its sickle cell treatments, including Oxbryta and osivelotor, another therapy secured from the Global Blood deal.
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder in which red blood cells become sickle- or crescent-shaped and can cause strokes, organ damage and death.
Existing FDA-approved therapies for the genetic blood disorder includes Vertex Pharmaceuticals' and CRISPR Therapeutics' Casgevy and Bluebird Bio's Lyfgenia.
(Reporting by Padmanabhan Ananthan in Bengaluru; Editing by Sahal Muhammed and Devika Syamnath)

AcquisitionClinical ResultDrug ApprovalPost-Marketing Study
100 Deals associated with bluebird bio, Inc.
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with bluebird bio, Inc.
Login to view more data
Corporation Tree
Boost your research with our corporation tree data.
login
or

Pipeline
Pipeline Snapshot as of 27 Feb 2026
The statistics for drugs in the Pipeline is the current organization and its subsidiaries are counted as organizations,Early Phase 1 is incorporated into Phase 1, Phase 1/2 is incorporated into phase 2, and phase 2/3 is incorporated into phase 3
Discovery
1
1
Preclinical
Phase 1
3
3
Phase 2
Approved
3
15
Other
Login to view more data
Current Projects
| Drug(Targets) | Indications | Global Highest Phase |
|---|---|---|
Betibeglogene autotemcel ( β-globin ) | Beta-Thalassemia More | Approved |
Elivaldogene Autotemcel (Bluebird Bio) ( ABCD1 ) | Adrenoleukodystrophy More | Approved |
MDR gene transfer(bluebird bio, Inc.) | Brain Cancer More | Phase 2 |
Autologous CD34+ HSC cells(Boston Children's Hospital) ( BCL11A ) | Anemia, Sickle Cell More | Phase 2 |
FH-MCVA2TCR T-cell therapy(bluebird bio, Inc.) ( Viral proteins ) | Merkel Cell Carcinoma More | Phase 2 |
Login to view more data
Deal
Boost your decision using our deal data.
login
or

Translational Medicine
Boost your research with our translational medicine data.
login
or

Profit
Explore the financial positions of over 360K organizations with Synapse.
login
or

Grant & Funding(NIH)
Access more than 2 million grant and funding information to elevate your research journey.
login
or

Investment
Gain insights on the latest company investments from start-ups to established corporations.
login
or

Financing
Unearth financing trends to validate and advance investment opportunities.
login
or

AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free